Wireless Lan Vs Wan
When it comes to networking terminologies, two commonly used terms are wireless Local Area Network (LAN) and Wireless Area Network (WAN). These terms are often heard in the context of setting up internet connections, but what exactly do they mean? And how do they differ from each other? Let’s delve into the details of Wireless LAN vs. WAN to gain a better understanding.
Credit: www.linkedin.com
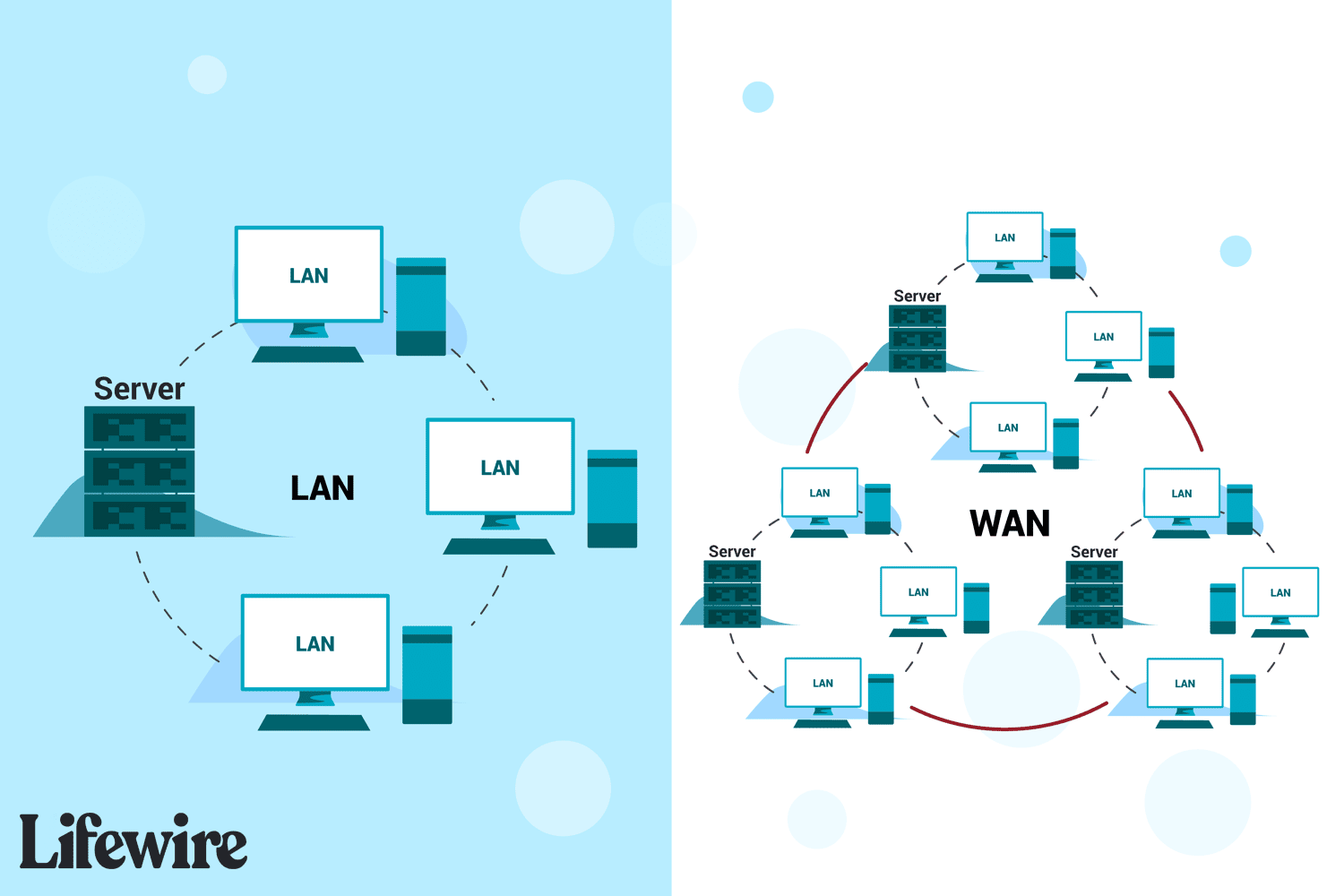
What is LAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and other devices in a limited area, such as a home, office, or school. LAN connections can be both wired, using Ethernet cables, or wireless, using Wi-Fi. A LAN is typically used for internal communication within an organization or a confined geographical area.
What is WAN?
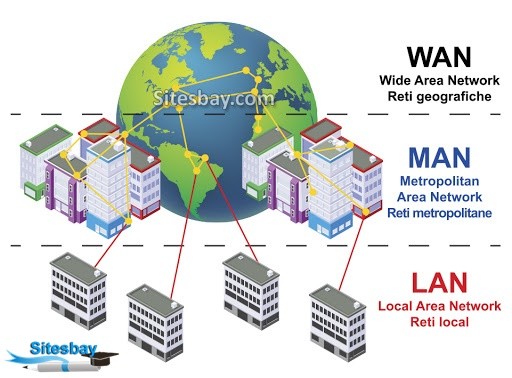
On the other hand, a Wide Area Network (WAN) extends over a large geographical area, connecting multiple LANs and other smaller networks together. WANs are used to connect devices that are spread across cities, countries, or even continents. The internet itself is a perfect example of a WAN.
Differences between Wireless LAN and WAN
Now that we understand the basic definitions, let’s explore the key differences between Wireless LAN and WAN in a structured manner:
| Aspect | Wireless LAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Local | Wide |
| Geographical Coverage | Small area: home, office, school | Large area: cities, countries, continents |
| Connectivity | Internally focused | Externally focused |
| Speed | Faster due to limited distance | Slightly slower due to larger coverage |
Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about network setups and configurations. While LAN is suitable for internal communication and local connectivity, WAN is essential for connecting geographically dispersed locations and facilitating external communications.
Credit: www.router-switch.com
Practical Applications
Let’s take a look at some practical scenarios where the choice between Wireless LAN and WAN becomes important:
- Setting up a Wi-Fi network at home involves implementing a Wireless LAN to connect personal devices within a limited area.
- Establishing connectivity between branch offices of a multinational corporation requires the use of a WAN to ensure seamless communication across different geographical locations.
Frequently Asked Questions For Wireless Lan Vs Wan
Do I Plug Wi-fi Into Lan Or Wan?
When connecting Wi-Fi, use the LAN port for devices within your network, and the WAN port for connecting to the wider internet network.
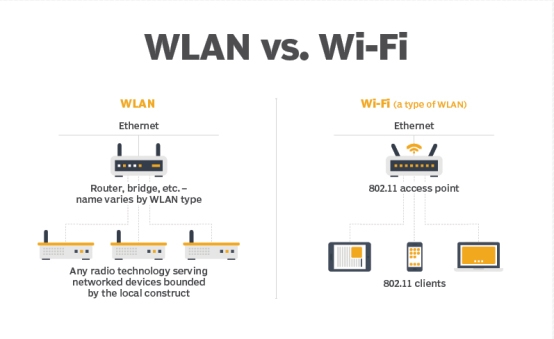
What Is The Difference Between Wan And Wlan?
The difference between WAN and WLAN is that WAN (Wide Area Network) spans a larger geographical area and connects multiple LANs together using technologies like leased lines or the internet. On the other hand, WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) is a wireless network confined to a smaller area such as a home, office, or campus, allowing devices to connect without wires.
WANs are used for long-distance communication, while WLANs are used for local wireless connectivity.
What Is The Difference Between Lan And Wlan?
A LAN uses local connections, while a WLAN is completely wireless with no wired connections. LANs are faster due to shorter distance and less congestion, while WANs cover wider areas and may be slightly slower.
Is Wireless Lan Just Wi-fi?
Yes, Wireless LAN includes Wi-Fi connections which are based on radio transmissions rather than wired connections.
Conclusion
Wireless LAN and WAN serve distinct purposes and play vital roles in shaping modern network infrastructures. By understanding the differences between the two, organizations and individuals can make well-informed decisions in selecting the appropriate type of network for their specific requirements.
Ultimately, both LAN and WAN are integral components of the digital connectivity landscape, and their significance will continue to grow as technology advances and global interconnectivity expands.
