What is the Main Difference between Wired And Wireless Networks
When it comes to establishing connectivity, understanding the differences between wired and wireless networks is crucial. Both forms of network have their own set of advantages and limitations. Let’s delve into the main disparities between them:
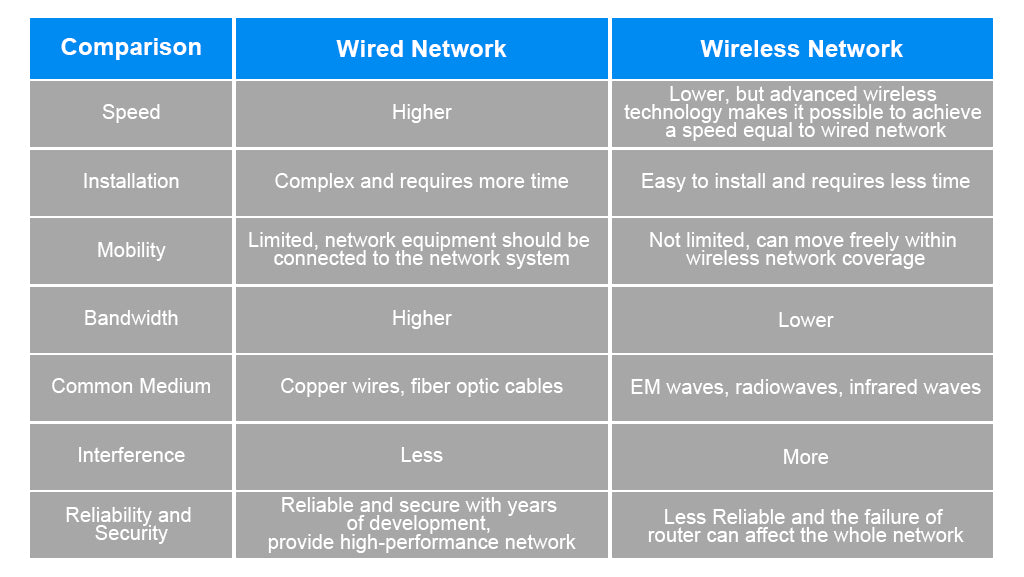
Stability and Reliability
In comparison to wireless networks, wired networks offer unparalleled stability and reliability. Physical cables, such as Ethernet or fiber optic cables, are used to establish connections. As a result, this type of network tends to provide a consistent and robust connection for data transfer. When reliability is the top priority, a wired network is usually the preferred choice.
On the other hand, wireless networks rely on radio waves for connectivity. While they provide greater mobility and flexibility, they are also more susceptible to interference, leading to potential reliability issues.
Data Transfer Speeds
In general, wired networks tend to offer faster data transfer speeds when compared to wireless networks. This can be attributed to the physical nature of the cable connections. With less susceptibility to interference and consistent signal transmission, wired networks excel in this aspect.
Conversely, wireless networks may experience slower data transfer speeds due to the potential for signal interference and environmental factors. This can impact the overall performance, especially in crowded or complex connectivity environments.

Credit: www.vcelink.com
Cost and Flexibility
When it comes to cost considerations, wired networks are often less expensive to set up initially. The required cables and switches are relatively affordable, making this option appealing for budget-conscious setups.
Wireless networks, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility and portability. Devices can connect without the constraint of physical cables, allowing for increased mobility and adaptability in various settings. This flexibility often comes with a slightly higher initial cost, mainly due to the advanced hardware required for wireless connectivity.
Credit: www.quora.com
Preference in Specific Contexts
Understanding the nature of your usage and the contextual requirements is crucial in determining the preference between wired and wireless networks. In scenarios that demand stable, high-speed connections with minimal interference, a wired network is the natural choice. Businesses or setups requiring consistent data transfer and reliability tend to favor this option.
For applications that prioritize mobility, adaptability, and the convenience of not being tethered to physical connections, wireless networks are the preferred choice. This is particularly relevant in settings where maneuverability and ease of setup are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Main Difference Between Wired And Wireless Networks
What Is The Difference Between Wireless And Wired Network?
The difference between wireless and wired networks is the method of connection. Wired networks use physical cables, offering stability and faster speeds. Wireless networks use radio waves, providing mobility and flexibility. Wired networks are reliable, while wireless networks are more susceptible to interference and have slower data transfer speeds.
What Is The Primary Difference Between A Hard Wired And Wireless Nos?
The primary difference between a hard-wired and wireless network is the method of connection. Hard-wired networks use physical cables like Ethernet or fiber optic cables, providing a more stable and faster connection. Wireless networks, on the other hand, use radio waves, allowing for more flexibility and mobility but may have slower speeds and potential interference.
Wired networks offer stability and speed, while wireless networks offer convenience and mobility.
What Is The Difference Between Wireless And Wired Network Interface Card?
The main difference between wired and wireless network interface cards is the method of connection. Wired NICs use physical cables for data transfer, providing stability and faster speeds, while wireless NICs use radio waves for connection, offering more flexibility in device mobility.
What Is The Difference Between Wired And Wireless Network Pdf?
A wired network uses physical cables, like Ethernet, for stable, fast connections. Wireless networks use radio waves for flexibility and mobility, but may have slower speeds and can face interference.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the main difference between wired and wireless networks lies in their stability, reliability, data transfer speeds, cost considerations, and adaptability in specific contexts. Both types of networks have their distinct advantages and limitations, and understanding these disparities is crucial in making informed decisions when it comes to establishing network connectivity.
By recognizing these differences, individuals and businesses can make sound choices that align with their specific networking requirements.
“` This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the main differences between wired and wireless networks, catering to a broad audience interested in network connectivity and technology. The objective analysis covers crucial aspects such as stability and reliability, data transfer speeds, cost considerations, and suitability in specific contexts.