What are the Four Types of Wireless Networks
Wireless networks play a crucial role in connecting devices and enabling communication without the need for physical wires. There are several types of wireless networks, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the different types of wireless networks is essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of wireless technology.

Credit: www.fortinet.com
Credit: www.oreilly.com
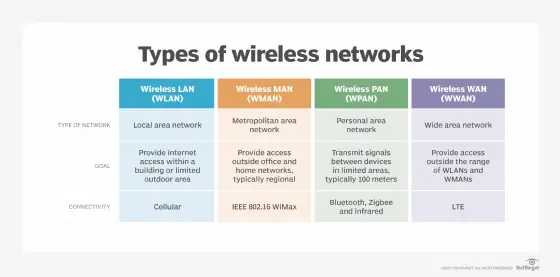
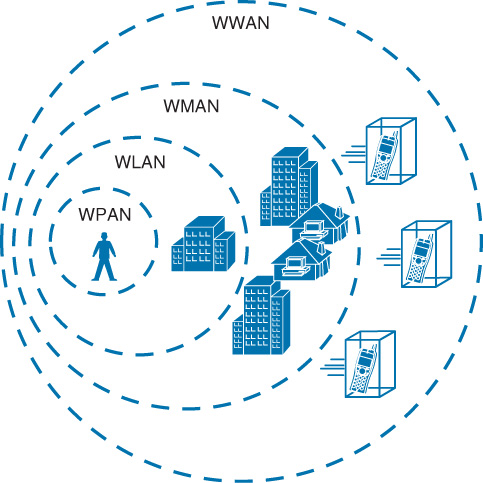
1. Wireless Local Area Networks (LAN)
Wireless LANs, also known as WLANs, are the most common type of wireless network. They are typically used to connect devices within a limited area, such as an office building, campus, or home. The technology behind WLANs allows for seamless connectivity and high-speed data transfer between devices. Examples of wireless LAN technologies include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee.
2. Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN)
Wireless MANs cover a larger geographical area compared to WLANs, often spanning across a city or metropolitan region. These networks are designed to provide wireless connectivity to a large number of users and often rely on technologies such as WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) to deliver high-speed internet access and other services over a wide area.
3. Wireless Personal Area Networks (PAN)
PANs are used for connecting devices within a person’s workspace or immediate surroundings, typically within a range of a few meters. Common applications of PANs include connecting smartphones to wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers. Bluetooth technology is a popular choice for establishing wireless PAN connections due to its low power consumption and versatility.
4. Wireless Wide Area Networks (WAN)
WANs cover a vast geographic area, often extending across cities, states, or even countries. These networks are critical for providing long-distance communication and enabling connectivity for remote locations. Cellular networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks are examples of technologies used to establish wireless WAN connections.
Difference Between Wired and Wireless Networks
While both wired and wireless networks serve the purpose of connecting devices, they differ in their mode of connection. Wired networks use physical cables to establish connections, whereas wireless networks rely on radio signals and electromagnetic waves for communication. The wireless nature of wireless networks enables greater flexibility and mobility compared to their wired counterparts.
Examples of Wireless Networks
Examples of wireless networks include cell phone networks, wireless local area networks (WLANs), wireless sensor networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks. Each type of wireless network serves specific purposes and has distinct requirements based on the intended usage and geographical coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The Four Types Of Wireless Networks
What Are The 5 Types Of Wireless Connection?
The five types of wireless connections are Wireless Personal Area Network (PAN), Wireless Local Area Network (LAN), Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Wireless Wide Area Network (WAN), and Wireless Mesh Network.
What Are Examples Of Wireless Networks?
Examples of wireless networks are cell phone networks, WLANs, wireless sensor networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks.
What Is The Most Common Type Of Wireless Network?
The most common type of wireless network includes wireless local area networks (LANs), wireless metropolitan area networks (MANs), wireless personal area networks (PANs), and wireless wide area networks (WANs). Each network has its own specific function and requires different equipment and connections.
What Are The 4 Major Differences Between Wired And Wireless Networks?
The 4 major differences between wired and wireless networks are: 1. Wired networks use physical cables for data transmission, while wireless networks use radio waves. 2. Wired networks generally have faster and more reliable connections compared to wireless networks. 3. Wired networks require cables to connect devices, while wireless networks allow for mobility and flexible connectivity.
4. Wired networks have a limited range, typically confined to the length of the cable, whereas wireless networks can cover larger distances depending on the strength of the signal.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of wireless networks is essential for building efficient and reliable communication systems. Whether it’s setting up a wireless home network or deploying a larger-scale wireless infrastructure, knowing the different network types and their applications is a fundamental aspect of modern connectivity.
