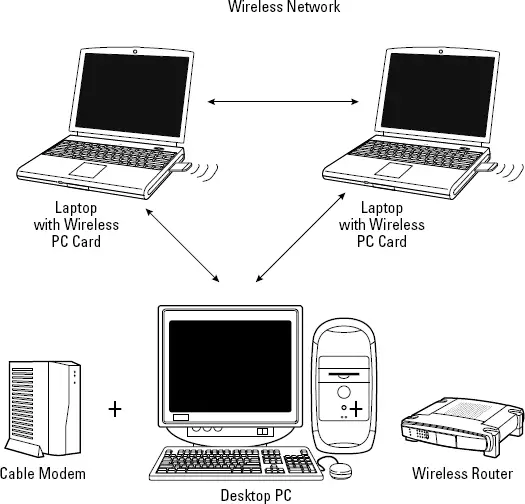
How Wireless Lan Works
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) have become an integral part of our daily lives, providing convenient access to the internet and allowing devices to communicate wirelessly over short distances. In this article, we will explore the basics of how wireless LANs work and the technologies behind them.

Credit: www.computernetworkingnotes.com
Wireless LAN Operation
A wireless LAN works by using radio frequency wireless technology to connect different devices within the network. Instead of relying on wired connections, devices communicate through radio transmissions. Here are some key aspects of how wireless LANs operate:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoding Data | Wireless LANs use encoding methods to convert data into a format suitable for transmission over radio waves. |
| Physical Hubs | In wireless LANs, physical hubs are replaced by access points, which act as central points for devices to connect to. |
| Carrier Sensing Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) | This technology allows devices to sense the wireless channel and avoid collisions when transmitting data. |
| Adding Wireless Clients | Devices that want to join a wireless LAN need to establish a connection with the access point by providing the required credentials. |
| Collision Avoidance | Wireless LANs implement mechanisms to avoid collisions by regulating when devices can transmit data. |
| Modulation | To achieve faster data transfer rates, wireless LANs use modulation techniques to encode data onto radio waves. |
| MIMO (Multiple In, Multiple Out) | MIMO technology involves using multiple antennas to improve data throughput and enhance wireless signal range. |
| Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) | OFDMA is a technique used in modern wireless LANs to increase the efficiency of data transmission by dividing the available frequency spectrum into multiple subchannels. |

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Types of Wireless Network
Wireless LANs can be classified into different network types, each serving various purposes. Let’s take a look at some common network types:
| Network Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) | An IBSS network, also known as an ad hoc network, allows devices to connect directly to each other without the need for an access point. |
| Infrastructure Mode | In infrastructure mode, devices connect to an access point that acts as a central hub for communication. This mode is commonly used in homes, schools, and businesses. |
| Multi-AP Infrastructure | In larger environments, multiple access points can be deployed to cover a wider area and ensure seamless connectivity throughout the network. |
| SSIDs | Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) are unique names assigned to wireless networks, allowing devices to differentiate between multiple networks in the same area. |
| Real-time and Non-real-time Traffic | Wireless LANs need to prioritize different types of traffic to ensure smooth operation. Real-time traffic, such as voice or video calls, requires higher priority compared to non-real-time traffic like email or web browsing. |
| Wireless LAN Controller | A wireless LAN controller manages and controls multiple access points within a network, providing centralized management and configuration capabilities. |
| Security and Quality of Service Attributes | Wireless LANs implement various security measures, such as encryption and authentication, to protect the network from unauthorized access. Quality of Service (QoS) attributes ensure that critical traffic receives higher priority for efficient delivery. |
| MAC Address Mapping | Media Access Control (MAC) address mapping is used to associate a device’s physical address with its IP address, allowing for proper routing and delivery of data within the network. |
Wireless LAN Technology Overview
Understanding the underlying technologies behind wireless LANs is essential. Here’s a brief overview:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Radio Frequency Wireless Technology | Wireless LANs operate on radio frequencies to transmit and receive data wirelessly. |
| Interference | One of the biggest challenges in wireless LAN technology is dealing with interference from other devices or neighboring networks operating on the same frequency. |
| Security | Wireless LANs implement security protocols to encrypt data transmitted over the network, preventing unauthorized access and eavesdropping. |
| SSID | The Service Set Identifier (SSID) is a unique name that identifies a specific wireless LAN network. |
| BSSID or Basic Service Set Identifier | A BSSID is a unique identifier assigned to each access point within a wireless LAN. |
| IBSS or Independent Basic Service Set | IBSS is a network type where devices can connect directly to each other without relying on an access point. |
| Transparent Roaming | This feature allows devices to seamlessly switch between access points without interrupting the connection. |
Advantages of Wireless LAN
Wireless LANs offer numerous advantages over traditional wired networks:
- Convenience: Wireless LANs provide the flexibility to access the network from anywhere within the coverage area.
- Scalability: It is easy to expand a wireless LAN by adding more access points to cover a larger area or accommodate more devices.
- Mobility: Users can move freely while staying connected to the network, enabling productivity on the go.
- Cost Savings: Wireless LANs eliminate the need for extensive cabling, reducing installation and maintenance costs.
- Flexibility: Devices can connect to a wireless LAN using different technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
In conclusion, wireless LANs have revolutionized the way we connect and communicate. Understanding how they work, the different network types, and the technologies involved is crucial in optimizing their usage and ensuring secure and efficient wireless connectivity.
source citation
Sources:
– CBT Nuggets: The Basics of Wireless LANs
– HowTo: Animation of Wireless LAN Working | How Packets are…
– Skyline ATS: Introduction to Wireless Network Types and How They Work
– Naj Qazi: Overview of Wireless LAN Tech
– How to Build a Wireless Home Network – Lifewire
– Cisco: What Is a Wireless LAN (WLAN)?
– TechTarget: What is the difference between WLAN and Wi-Fi?
– eSecurity Planet: How does wireless LAN security work?
– Aruba Networks: What Is a Wireless LAN (WLAN)?
– O’Reilly: Understanding How a Wireless LAN Works
Frequently Asked Questions For How Wireless Lan Works
Can You Do Lan Wirelessly?
Yes, you can do LAN wirelessly through a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network). A WLAN is a group of networked computers or devices that form a network using radio transmissions instead of wired connections. It operates using Wi-Fi technology, which allows for wireless connectivity within a close physical proximity.
WLANs are commonly found in homes, schools, and businesses.
Is Wireless Lan Just Wi-fi?
Yes, a wireless LAN (WLAN) is a group of computers or devices forming a network through radio transmissions, and Wi-Fi is a type of WLAN. Wireless LAN uses radio technology to connect nodes, while Wi-Fi refers to a specific wireless technology within a WLAN.
What Is The Difference Between Wi-fi And Wireless Lan?
Wi-Fi is a type of WLAN. WLAN uses radio tech to connect nodes, while Wi-Fi is a specific type of WLAN.
How Does Wireless Lan Security Work?
Wireless LAN security protocols encrypt data to prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping, with authentication mechanisms to verify users’ identities.
